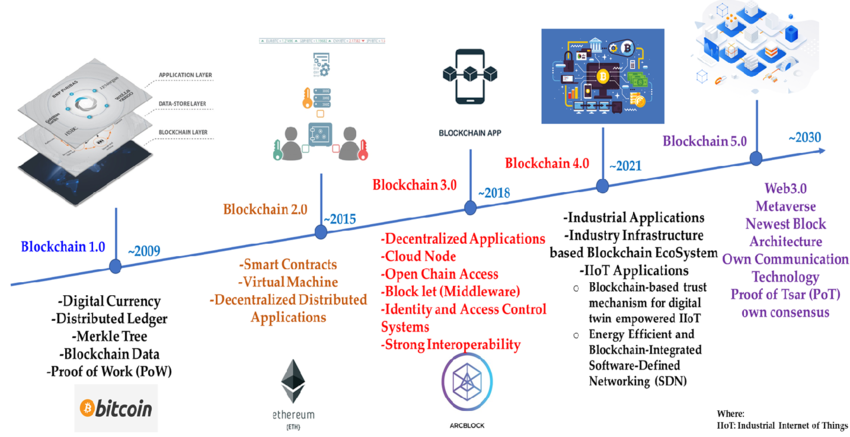
Understand Blockchain: A Comprehensive Guide
The so-called blockchain technology is but another innovation in the world surrounding cryptocurrencies online, such as Bitcoin. Its structure and a wide array of possibilities for its application make it outstandingly hot, not only with technologists but with economists and businesses. So, this paper will take a closer look at blockchain technology, how it works, while giving some of the potential implications across the various sectors.
What is Blockchain?
Generally, a blockchain is a decentralized digital register that records transactions on a number of computers in such a way that the data becomes very difficult to corrupt because of its security, transparency, and immutability. At least, blockchains work with distributed technology unlike traditional databases managed by an entity. In the case of blockchains, each node—referred to as nodes—reproduces the whole blockchain at his disposal. In its essence, it does not allow a single point of failure or corruption in the data.
The term “blockchain” itself comes from the structure: data is kept within blocks, and each block has a connection to its precedent, thereby creating a chain. This chain of blocks is cryptographically sealed so that once data goes in, computationally it is impractical to change this and not affect everything further down the line.
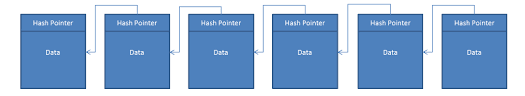
How does Blockchain Work?
Understanding how blockchain works requires a peek into its key components and the processes that enable its functionality:
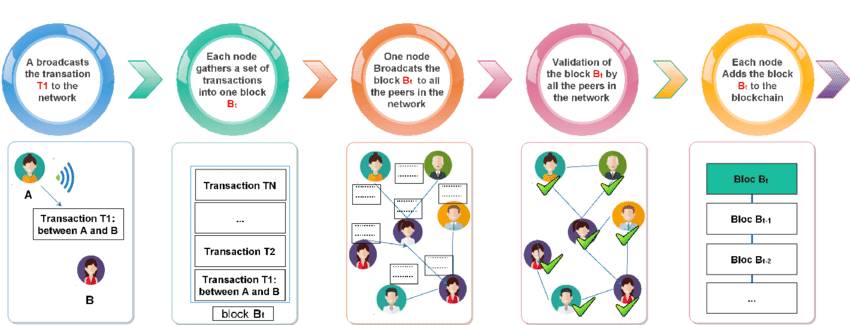
1. Blocks:
A Blockchain is made of blocks. Each block contains a list of transactions. During the process, when a transaction takes place, it is grouped along with other transactions to form a block. Consequently, the block is broadcasted across a network for validation.
2. Nodes:
Any single computer taking part in a blockchain network is called a node. Each node keeps a copy of the blockchain to provide self-consistency in data maintained over a network. Nodes also validate new transactions and blocks.
3. Consensus Mechanism:
A consensus mechanism is utilized to ensure that all nodes within a blockchain network agree concerning the current state of the blockchain. The most popular consensus mechanisms to this date are the Proof of Work and Proof of Stake. The former, PoW, provides nodes with an independent competitive way of solving complex mathematical problems, where the first node to solve it earns the right to add the new block into the chain and a certain reward. In PoS, validators would be chosen depending on the number of coins they hold and are willing to “stake” as collateral.
4. Hashing:
Each block bears a unique code, the ‘hash,’ created from the data of that block and the hash of the previous block. This hashing process assures the integrity of the data. When any information in a block is changed, so does its hash; in breaking the chain, it serves to warn the network of possible tampering.
5. Immutability:
Perhaps this is the inherent characteristic or the core property of a blockchain. In a blockchain, once a block is added, it cannot be changed or deleted. Therefore, blockchain provides ideal technology for applications where data integrity and transparency are prime requirements.
Types of Blockchain
There can be different types of blockchains, serving different purposes:
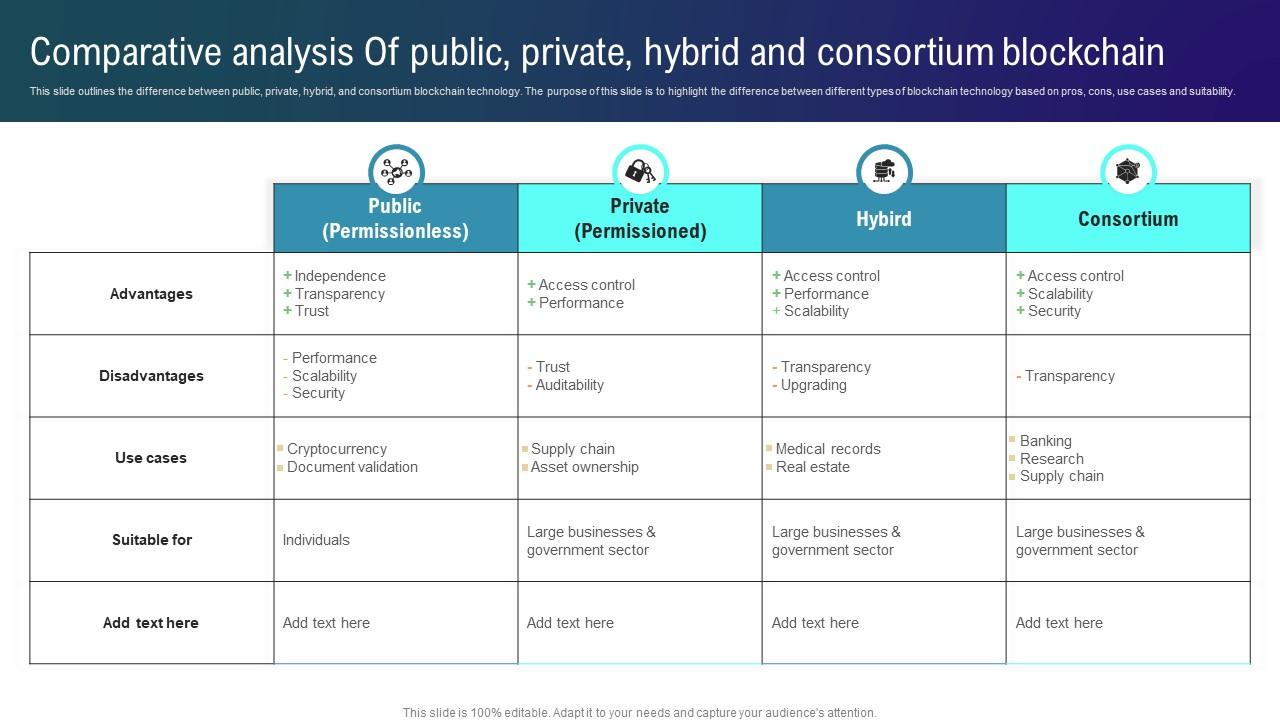
1. Public Blockchains:
They are open to any individual or organization willing to join the network. Public blockchains are decentralized; therefore, no single entity will have control over the network. Examples of public blockchains include Bitcoin and Ethereum.
2. Private Blockchains:
These are blockchains whose participation is restricted to a selected few, unlike their public blockchain counterparts. Typically, they are used by businesses or organizations that want more control over the access of transactions and their validation. Compared to public chains, private blockchains are faster and more scalable but less decentralized.
3. Consortium Blockchains:
This is a mix of public and private blockchains. It is governed by a group of organizations, not one single organization, which has to make it decentralized while controlled. These blockchains are mostly used in industries where multiple organizations need to work together and share data securely.
4. Hybrid Blockchain:
This type of blockchain borrows characteristics from both public and private blockchains, providing a more customizable approach to be open to the public or private, depending on what the participants of this network want to share with the world at large.
Applications of Blockchain Technology
Blockchain’s versatility has seen it adopted by various sectors in toto—all of them leveraging on their unique features to solve particular problems.
1. Cryptocurrencies:
Blockchain technology is first and foremost applied in cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin and Ethereum. This provides a secure, transparent, and decentralized way for transactions not requiring any intermediary like banks.

2. Supply Chain Management:
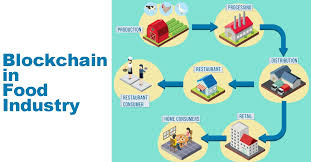
It traces product history from the place of its origin to the consumer, making it transparent and reducing the risks of fraud. This is how blockchain in the food industry will be able to trace the origin of a contaminated product. That would mean faster recalls and more consumer trust.
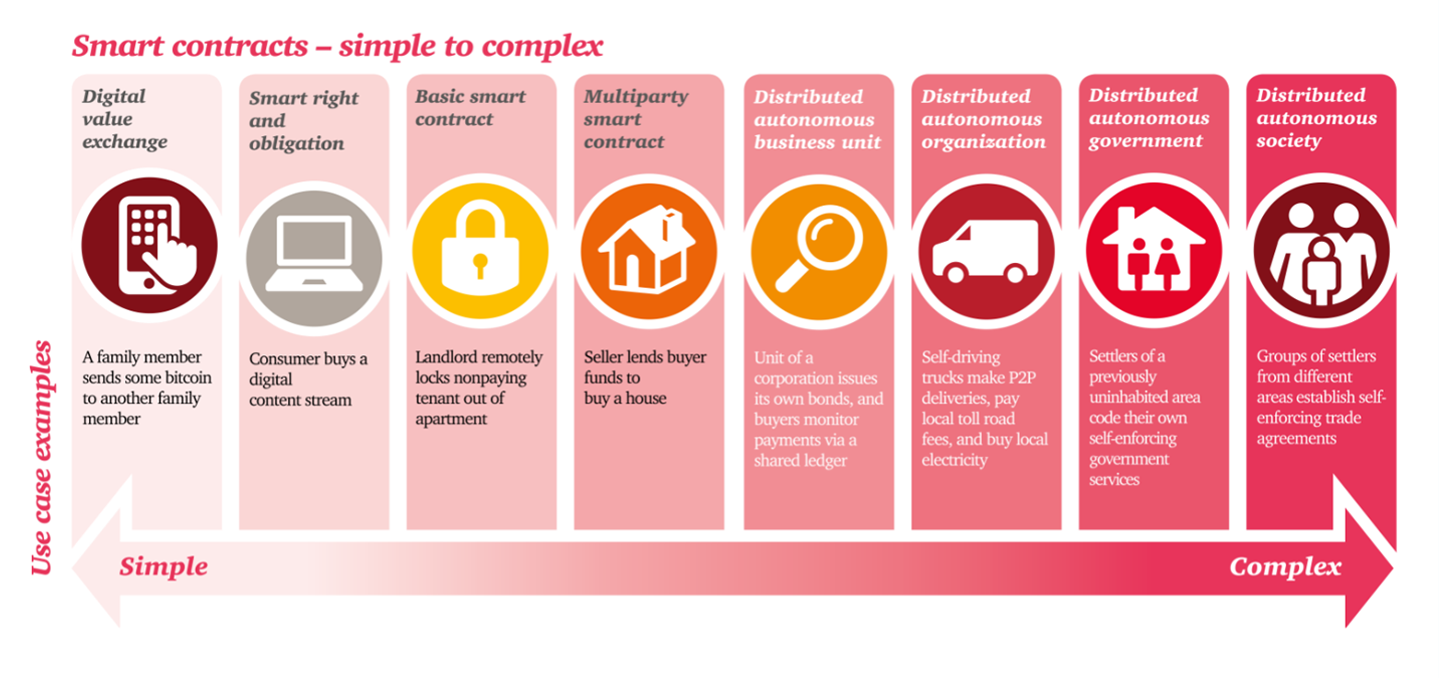
3. Smart Contracts:
Smart contracts are self-executing contracts with the terms of the agreement directly written into code. These contracts automatically execute when conditions are met, therefore eliminating the need for intermediaries and reducing the risk of human error or manipulation.
4. Healthcare:
Blockchain in healthcare can secure patient records, hence making the data only available to the authorized persons. This would result in a management system of enhanced medical records while offering protection to the privacy of patients.
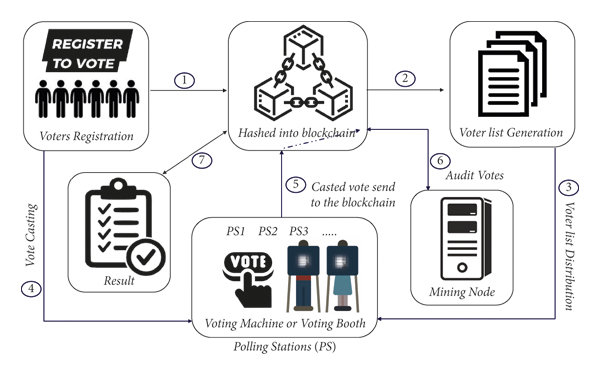
5. Voting systems:
Blockchain can be used to develop secure and transparent e-voting systems when capturing the opinion of voters; this might consequently reduce electoral fraud and increase the confidence of voters in the process.
6. Finance and Banking:
Blockchain can make a number of financial processes easier, such as cross-border payments. This is because it eliminates the requirement for any middlemen involved in transactions while reducing transaction times and costs. This also increases security with an open, tamper-proof record of transactions.
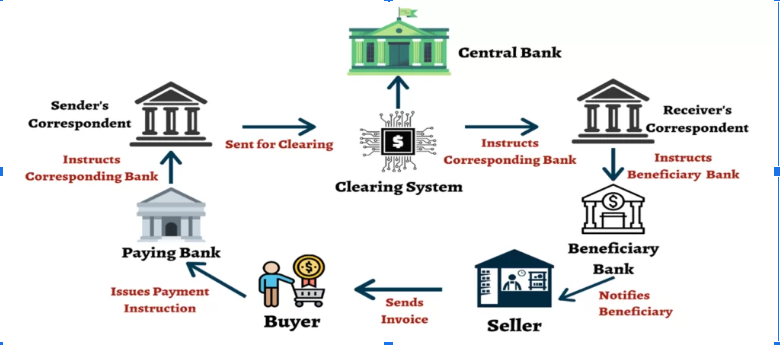
7. Real Estate:
To this regard, blockchain can facilitate an easier way of purchase and sale of property. It offers a clear, undeniable record of ownership and historical transaction record concerning the property. This would reduce the possibilities of fraud and make the process more efficient.

Challenges and Limitation of Blockchain
Best-case scenario, blockchain technology is not free of some challenges and limitations:
1. Scalability:
With every new transaction, the ledger size increases; this is quite an unpleasant scenario wherein with each increase in transactions comes decreased processing time and increased storage space. Thus, it creates one of the greater challenges to public blockchains since they have to hold a large number of users.2. Energy Consumption:
The consensus mechanism, especially that of Proof of Work, requires many computations. In turn, it consumes a lot of energy, raising concerns about the impact of blockchain technology on the environment.
3. Regulation and Legal Issues:
The decentralized nature of blockchain raises problems for regulators who find it very hard to apply pre-existing legal frameworks to systems built on blockchain. Data privacy, security, and jurisdiction are some of the issues to be ascertained as this technology advances further.
4. Interoperability:
A very hard task is enabling the transfer of assets or data from one blockchain to any other blockchain and is an open research item.
5. Adoption Barriers:
For realizing the potential promise of growth of blockchain, it necessarily requires wide adoption. The introduction of the technology is in its early stages of development, and several organizations are adjudging its adoption due to a lack of understanding about its implementation and security concerns.The Future of Blockchain
The future holds much promise for blockchain technology, and there is still continued research and development to achieve what it lacks at present. Some indications are:

1. Scalability Solutions:
Several possible scalability solutions to be implemented on the blockchain are under research, such as sharding, layer-2 protocols, and consensus mechanisms of increased performance.
2. Complementary integration with other emerging technologies:
Blockchain is increasingly integrating, actually complementing, leading technologies in areas like artificial intelligence, IoT, and DeFi. In this regard, some integrations will further create scope for new use cases and innovation in and around life itself.3. Regulatory Frameworks:
Governments and regulatory institutions are growing into developing systems that take into account the legal and security viability of blockchain technology as it fosters innovation.4. Increased Adoption:
As more and more businesses and industries come to recognize the scope of potential benefits the technology entails, adoption will increase. This, in return, will give rise to new business models, greater process efficiencies, increased security, and a more transparent digital economy.
Conclusion
Blockchain technology is a disruptor, decentralizing many industries safely and transparently with digital upheaval. Though in its infancy and riddled with manifold challenges, it is soon going to sail out of these problems through continuous research and development for a wider reach and newer applications. In its not-so-distant future, blockchain is going to be the backbone of the digital economy and provide new opportunities for businesses, governments, and individuals. Understanding the basic concepts of blockchain, its mechanisms, and probable applications explains the effect this technology will have on the world. Be it an entrepreneur, technologist, or simply somebody who is fascinated by how technology will change the world in the next decade, staying updated about blockchain will undoubtedly be part of navigating successfully in tomorrow’s digital world.